Medications for Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. This article explores the various medications for diabetes, their functions, and how they contribute to effective diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. There are two primary types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type requires insulin therapy for survival.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. This type is more common and can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medication.
Types of Medications for Diabetes
Diabetes medications are designed to help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Here are the main categories of diabetes medications:
- Insulin TherapyInsulin is essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes and may be required for those with Type 2 diabetes who cannot control their blood sugar with other medications. Insulin can be administered in several forms, including:
- Rapid-acting insulin: Begins working within minutes and is used before meals.
- Short-acting insulin: Takes effect within 30 minutes and is used for mealtime control.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: Covers insulin needs for about half a day or overnight.
- Long-acting insulin: Provides a steady level of insulin throughout the day and night.
- Oral MedicationsOral medications are commonly used for Type 2 diabetes and can work in various ways to reduce blood sugar levels:
- Metformin: Often the first medication prescribed for Type 2 diabetes, metformin reduces glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: Stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin. Examples include glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride.
- Meglitinides: Similar to sulfonylureas but faster acting, helping the pancreas release more insulin in response to meals. Examples include repaglinide and nateglinide.
- Thiazolidinediones: Improve insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat tissues. Examples include pioglitazone and rosiglitazone.
- DPP-4 inhibitors: Help reduce blood sugar levels by preventing the breakdown of incretin hormones. Examples include sitagliptin and saxagliptin.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: Help the kidneys remove glucose from the bloodstream. Examples include canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin.
- Injectable MedicationsBesides insulin, there are other injectable medications used to manage diabetes:
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: These medications mimic the incretin hormone, which increases insulin release, decreases glucagon release, and slows gastric emptying. Examples include liraglutide, exenatide, and semaglutide.
- Amylin analogs: Pramlintide is an example that helps control blood sugar by slowing gastric emptying and suppressing glucagon.
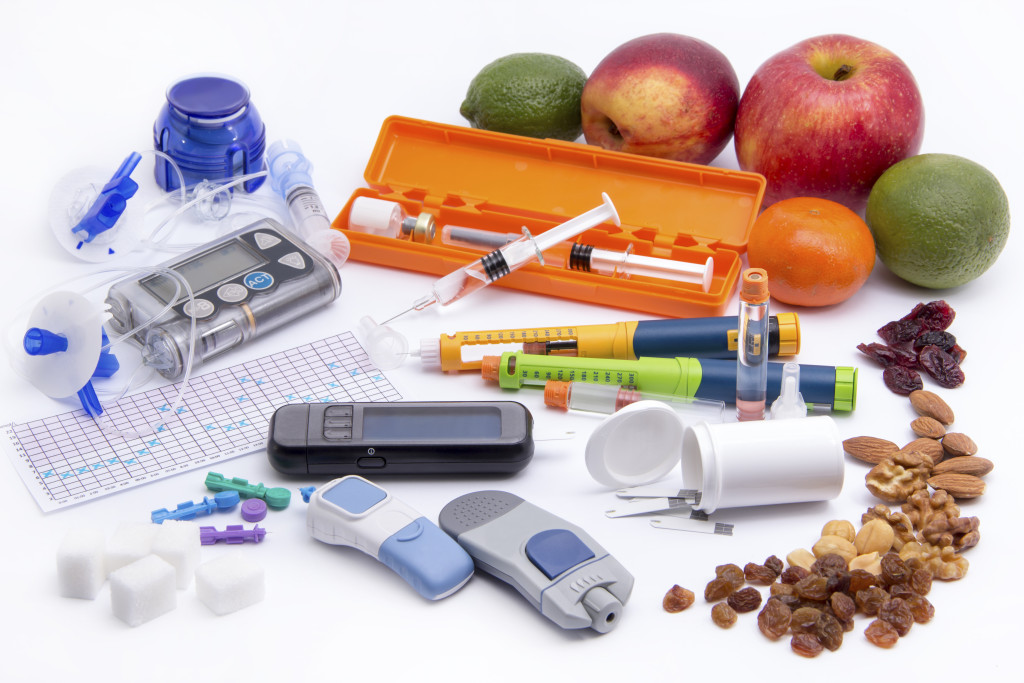

How Medications for Diabetes Work
Each category of diabetes medication works through different mechanisms to achieve blood sugar control:
- Increase Insulin Production: Medications like sulfonylureas and meglitinides stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- Improve Insulin Sensitivity: Metformin and thiazolidinediones help the body’s cells respond better to insulin.
- Reduce Glucose Production: Metformin decreases the amount of glucose produced by the liver.
- Increase Glucose Excretion: SGLT2 inhibitors help the kidneys remove glucose from the body through urine.
- Slow Carbohydrate Absorption: Medications like alpha-glucosidase inhibitors slow the absorption of carbohydrates in the intestines.
- Mimic Hormonal Effects: GLP-1 receptor agonists and amylin analogs mimic hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Diabetes Medications
Effective diabetes management with medications can lead to numerous health benefits:
- Blood Sugar Control: Proper medication use helps maintain blood sugar levels within a target range.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Managing blood sugar levels can prevent or delay complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and eye problems.
- Improved Quality of Life: Controlling diabetes can enhance overall health and well-being, allowing individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Managing Diabetes with Medication
Successfully managing diabetes with medication requires a comprehensive approach:
- Adherence to Prescribed Medications: Taking medications as directed by a healthcare provider is crucial for effective blood sugar control.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of blood sugar levels helps in making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Combining medication with a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management can significantly improve diabetes outcomes.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider ensure that the treatment plan is effective and allows for timely interventions if needed.
For a wide range of diabetes management products and expert advice, visit weightlossandfatloss.com.
Conclusion
Medications for diabetes are vital tools in managing this chronic condition. Understanding the different types of medications and how they work can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plans. Whether it’s insulin therapy, oral medications, or injectables, each plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications. By combining these medications with a healthy lifestyle and regular medical care, individuals with diabetes can lead healthier, more active lives.

Appel à l'action
Ready to take control of your diabetes management? Explore our range of products and resources at weightlossandfatloss.com and find the support you need to manage your diabetes effectively.